mirror of
https://github.com/lephisto/pfsense-analytics.git
synced 2026-01-26 12:14:08 +01:00
Updated Docs
This commit is contained in:
98
README.md
98
README.md
@@ -16,18 +16,16 @@ This walkthrough has been made with a fresh install of Ubuntu 18.04 Bionic but s
|
|||||||
Install docker, docker-compose and git.
|
Install docker, docker-compose and git.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
ubuntu@pfanalytics:~$ sudo apt install docker.io docker-compose git
|
sudo apt install docker.io docker-compose git
|
||||||
...
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Prepare Docker
|
# 1. Prepare Docker
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Let's pull this repo to the Server where you intend to run the Analytics front- and backend.
|
Let's pull this repo to the Server where you intend to run the Analytics front- and backend.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
git clone https://github.com/lephisto/pfsense-graylog
|
git clone https://github.com/lephisto/pfsense-analytics
|
||||||
cd pfsense-graylog
|
cd pfsense-analytics
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We have to adjust some Systemlimits to allow Elasticsearch to run:
|
We have to adjust some Systemlimits to allow Elasticsearch to run:
|
||||||
@@ -50,10 +48,25 @@ The URL you want your Graylog to be available under:
|
|||||||
A Salt for encrypting your Gralog passwords
|
A Salt for encrypting your Gralog passwords
|
||||||
- GRAYLOG_PASSWORD_SECRET (Change that _now_)
|
- GRAYLOG_PASSWORD_SECRET (Change that _now_)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now spin up the stack with:
|
|
||||||
|
Now We need to pull the GeoIP Database from maxmind:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
docker-compose up
|
curl --output mm.tar.gz https://geolite.maxmind.com/download/geoip/database/GeoLite2-City.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
tar xfzv mm.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
.. symlink (take correct directory, includes date..):
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
ln -s GeoLite2-City_20191105/GeoLite2-City.mmdb .
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Finally, spin up the stack with:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
sudo docker-compose up
|
||||||
```
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
This should expose you the following services externally:
|
This should expose you the following services externally:
|
||||||
@@ -67,9 +80,9 @@ This should expose you the following services externally:
|
|||||||
Depending on your Hardware after a few minutes you should be able to connect to
|
Depending on your Hardware after a few minutes you should be able to connect to
|
||||||
your Graylog Instance on http://localhost:9000. Let's see if we can login with username "admin", password "admin".
|
your Graylog Instance on http://localhost:9000. Let's see if we can login with username "admin", password "admin".
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Indices
|
# 2. Initial Index creation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
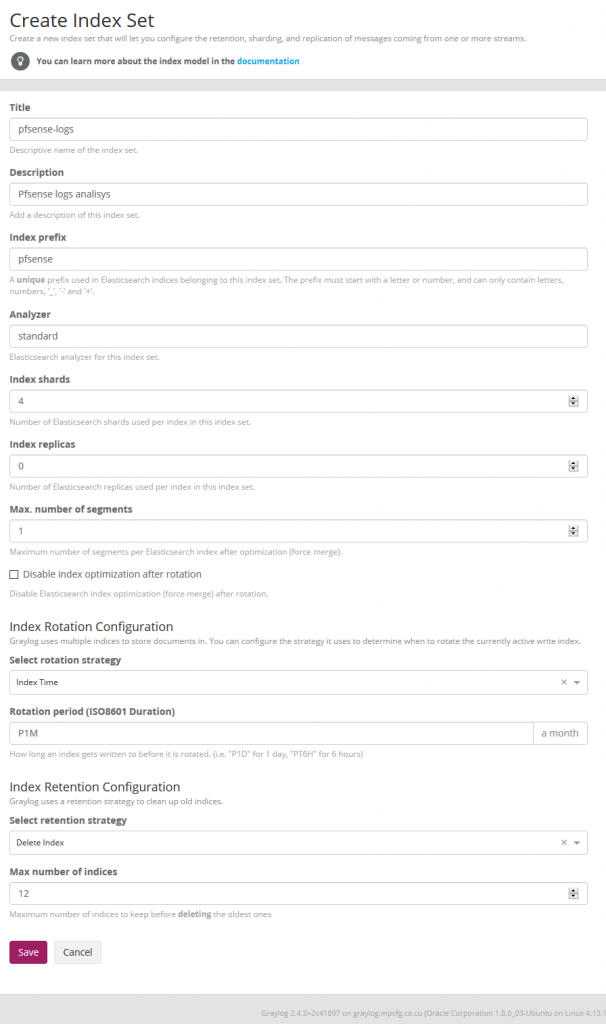
We now have to create the Indices in Elasticsearch for the Pfsense logs in System / Indexes
|
We now have to create the Indices in Elasticsearch for the pfSense logs in System / Indices
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
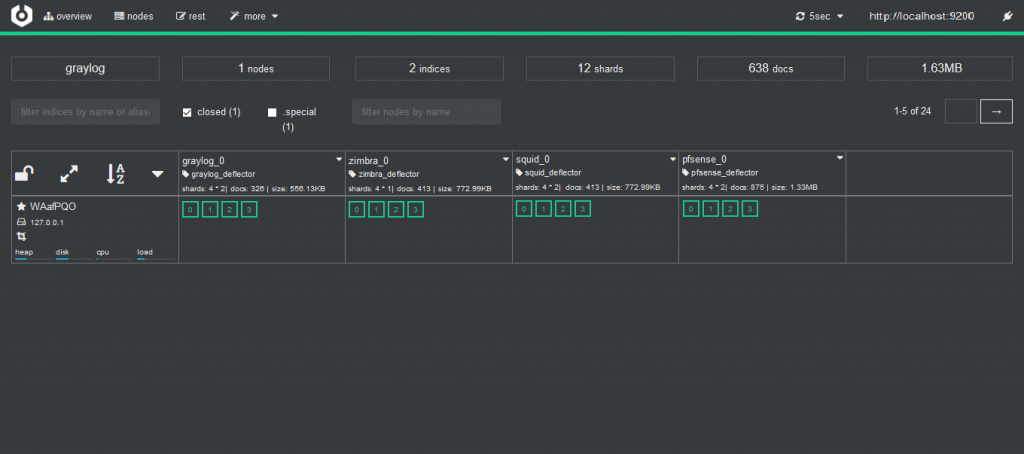
@@ -81,13 +94,25 @@ and with [cerebro](https://github.com/lmenezes/cerebro) we can check it. You can
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Content Pack
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In Graylog go to System->Configurations and:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. Change the order by Message processors, to have "GeoIP Resolver on the bottom"
|
||||||
|
2. Update Plugins an denable Geo-Location Processor
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# 4. Content Packs
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Custom Content Pack
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
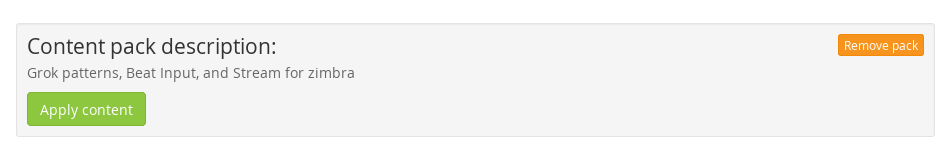
This content pack includes Input rsyslog type , extractors, lookup tables, Data adapters for lockup tables and Cache for lookup tables.
|
This content pack includes Input rsyslog type , extractors, lookup tables, Data adapters for lockup tables and Cache for lookup tables.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
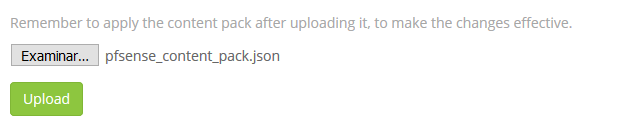
We can take it from the Git directory or sideload it from github to the Workstation you do the deployment on:
|
We can take it from the Git directory or sideload it from github to the Workstation you do the deployment on:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
https://github.com/lephisto/pfsense-graylog/raw/master/pfsense_content_pack/graylog3/3-pfsense-analysis.json
|
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/lephisto/pfsense-analytics/master/pfsense_content_pack/graylog3/pfanalytics.json
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -104,7 +129,7 @@ And we apply it
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Streams
|
# 4. Assign Streams
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We edit the stream of pfsense in Streams to associate the index that we created initially. We mark that it eliminates the coincidences for the default stream 'All message' so that only it stores it in the index of pfsense.
|
We edit the stream of pfsense in Streams to associate the index that we created initially. We mark that it eliminates the coincidences for the default stream 'All message' so that only it stores it in the index of pfsense.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -114,7 +139,7 @@ We edit the stream of pfsense in Streams to associate the index that we created
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
This part might be a little bit confusing, so read carefully!
|
This part might be a little bit confusing, so read carefully!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
As previously explained, by default graylog for each index that is created generates its own template and applies it every time the index rotates. If we want our own templates we must create them in the same elasticsearch. We will add the field real_timestamp that will be useful when using grafana and we also convert the geo type dest_ip_geolocation and src_ip_geolocation to type geo_point to be used in the World Map panels since graylog does not use this format.
|
As previously explained, by default graylog for each index that is created generates its own template and applies it every time the index rotates. If we want our own templates we must create them in the same elasticsearch. We will convert the geo type dest_ip_geolocation and src_ip_geolocation to type geo_point to be used in the World Map panels since graylog does not use this format.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Get the Index Template from the GIT repo you cloned or sideload it from:
|
Get the Index Template from the GIT repo you cloned or sideload it from:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -146,29 +171,10 @@ We start the graylog service again and this will recreate the index with this te
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
`sudo docker-compose start graylog`
|
`sudo docker-compose start graylog`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Pipelines
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The pfsense logs that arrive at graylog, the date and the time are not sent to it, storing in the timestamp field the time they arrive at the graylog itself and this date and time is in UTC format so we must modify it so that it does not there are interpretation problems in grafana time format when displaying them.
|
# 6. Configure pfSense
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We need to edit the pipeline of pfsense then in System/Pipelines
|
We will now prepare Pfsense to send logs to graylog and for this in Status/System Logs/ Settings we will modify the options that will allow us to do so.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Source of the rule that makes the adjustment of the timestamp that we are going to use in grafana:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
rule "timestamp_pfsense_for_grafana"
|
|
||||||
when
|
|
||||||
has_field("timestamp")
|
|
||||||
then
|
|
||||||
// the following date format assumes there's no time zone in the string
|
|
||||||
let source_timestamp = parse_date(substring(to_string(now("America/Habana")),0,23), "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS");
|
|
||||||
let dest_timestamp = format_date(source_timestamp,"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
|
|
||||||
set_field("real_timestamp", dest_timestamp);
|
|
||||||
end
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We save and we have the pipeline ready to later receive the first logs.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Pfsense
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We will now prepare Pfsense to send the log logs to the graylog and for this in Status/System Logs/ Settings we will modify the options that will allow us to do so.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We go to the Remote Logging Options section and in Remote log servers we specify the ip address and the port prefixed in the content pack in the pfsense input of graylog that in this case 5442.
|
We go to the Remote Logging Options section and in Remote log servers we specify the ip address and the port prefixed in the content pack in the pfsense input of graylog that in this case 5442.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@@ -184,24 +190,4 @@ We now go to graylog by selecting the pfsense stream and we will see how it is p
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
# Grafana
|
# Grafana
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Graylog dashboards do not offer the possibilities to my way of seeing that grafana has so our dashboard will do in grafana.
|
Dashboards and Datasource are auto-provisioned to Grafana. Log in at http://localhost:9000 with admin/admin and you should see your Firewall Logs pouring in.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We create the datasource in grafana which we will name Pfsense-Graylog
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
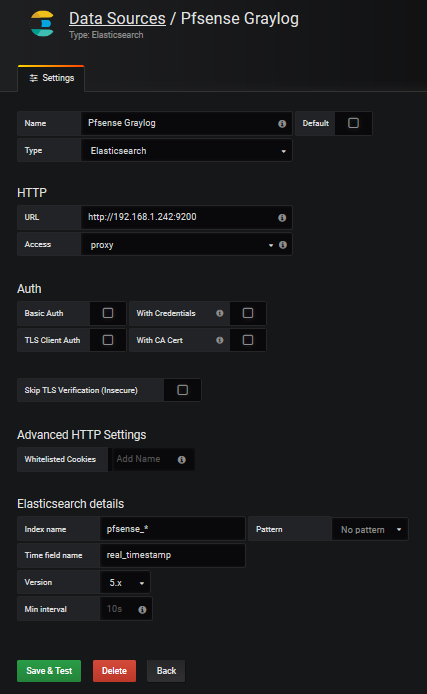
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
I share with you a [predesigned dashboard](https://grafana.com/dashboards/5420) in the official grafana site which could be imported.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
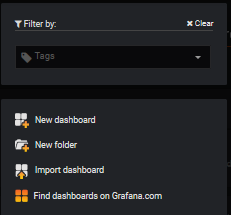
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We select Import dashboard
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
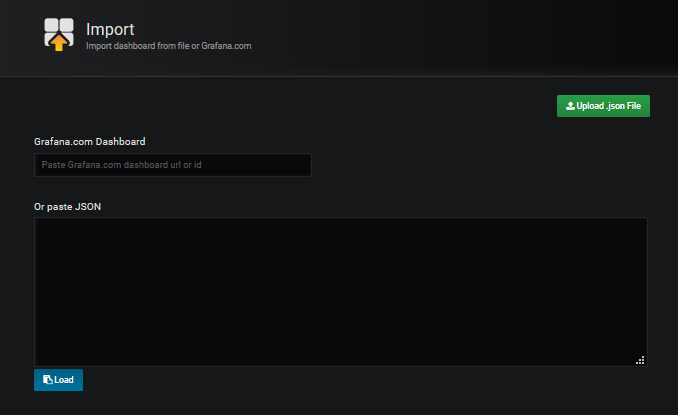
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We upload the downloaded file Upload .json file and associate it with the datasource created for it.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
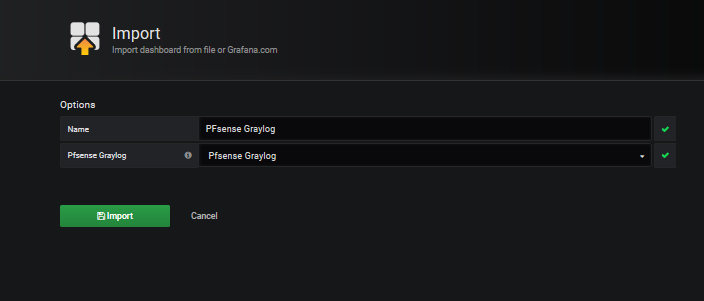
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
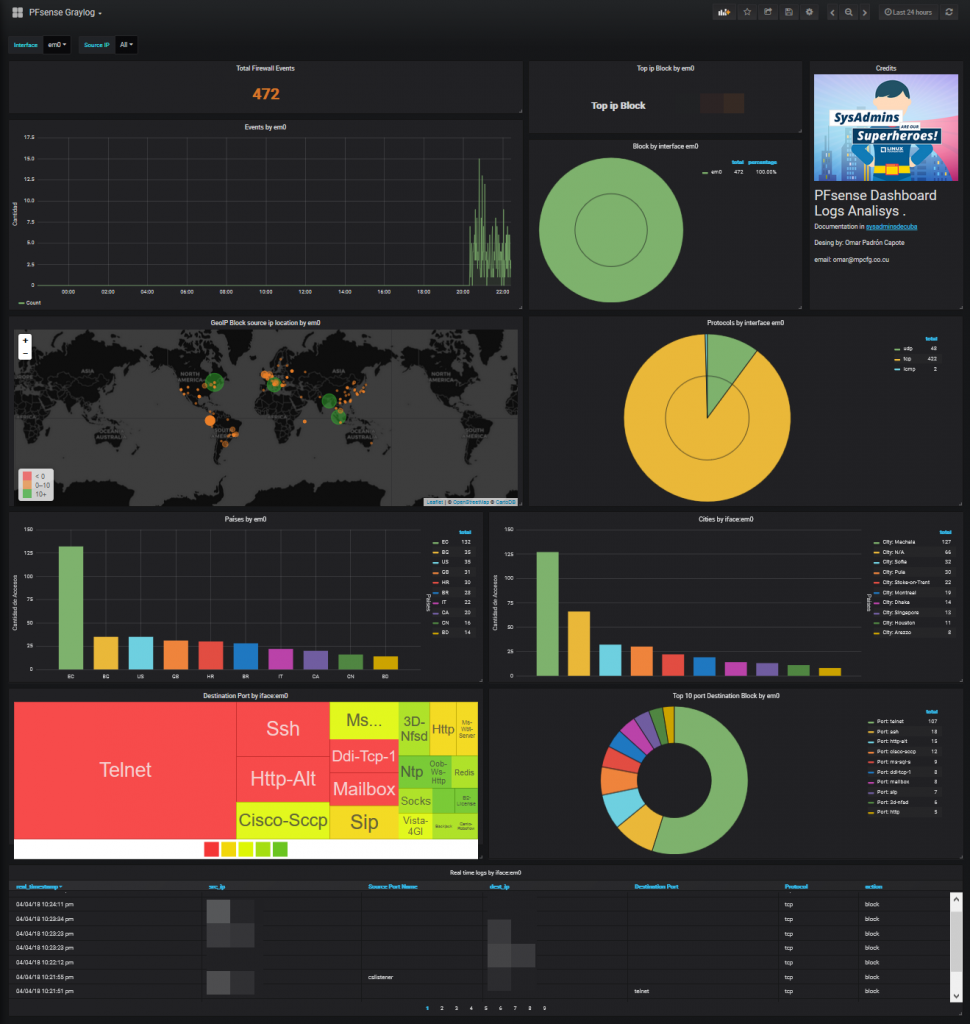
We can already see the dashboard in action.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user